Purpose of running this test:
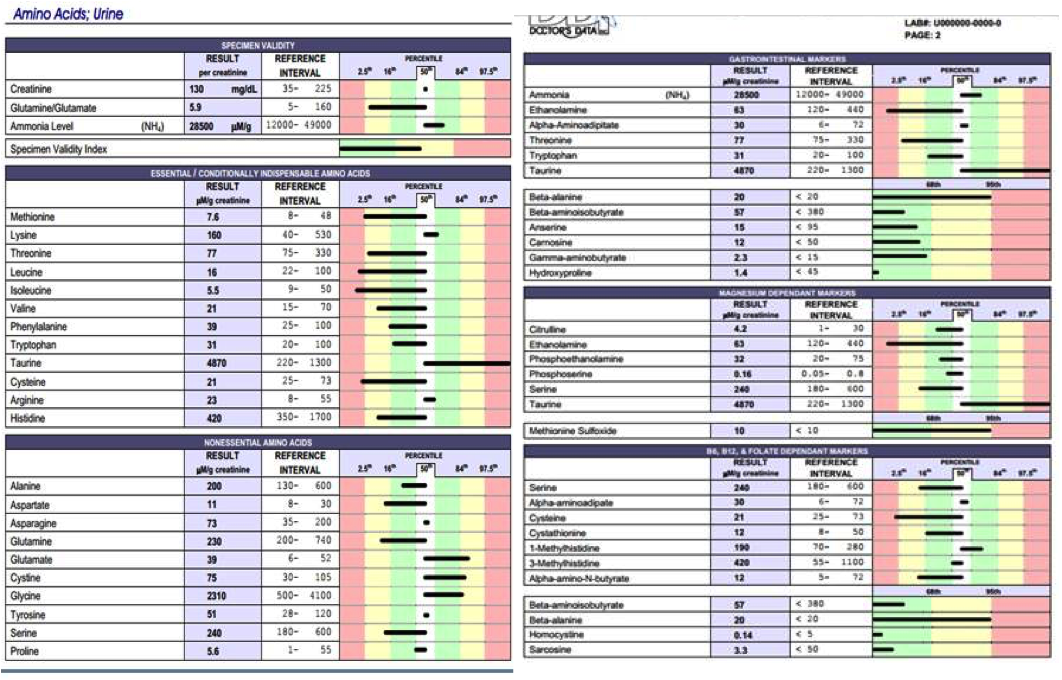
The Urine Amino Acids Test gives you information about amino acids, the building blocks for the proteins in your body. Essential amino acids are those which must be in your diet. Your body cannot synthesize these. Non-essential amino acids are those which can be synthesized from other constituents, given that the substrates necessary for their formation are present in your body.
The genetic information that is stored and transmitted in the four-letter alphabet and language of DNA is ultimately expressed in the twenty-letter language of proteins. All proteins, whether from the most ancient lines of bacteria or from the most complex forms of life, are constructed from the same ubiquitous set of twenty amino acids, linked in characteristic sequences. These amino acids are precursor molecules to protein structures with strikingly different properties and activities. From these building blocks, these relatively simple subunits, your body makes such widely diverse structures as enzymes, hormones, antibodies, transporters, muscle fibers, and the lens portion of the eye.
The Urine Amino Acids Test gives you a sense of the overall nutrient absorption from your gastrointestinal tract (GI tract), as well as shows you how well you are doing with the compounds in your methylation cycle. It measures homocysteine, an important indicator of cardiac health and pro inflammatory status in your body, and a component of the methylation cycle. It also measures methionine, taurine, phospholipids, and other compounds which are indicators of methylation cycle status. It gives you a sense of your ability to make methyl groups by measuring the level of molecules that need methyl groups to be processed.
| Amino Acid | This table contains the rationale behind my suggestions. These suggestions are for your consideration. Defer your choices to your own health care practitioner, as always. |
| Creatinine | A high level of creatinine means that your urine is very concentrated. This may mean that your kidneys are under additional stress. In this case consider the use of Kidney Support nucleotide blend, Ora-Kidney, Dandelion Leaf, Rhodiola, SHMT Spray, AHCY/SHMT compound, and Zinc Lozenges. If your pH is low, consider using sodium bicarbonate to help balance the ph as well as to normalize creatinine levels.Creatinine levels that are low suggest insufficient methylation and a need for SAM-e. Low levels of creatine have been associated with limited language development, so you can consider using Creatine plus SAM-e. If your creatinine is chronically high, consider checking your blood sugar levels. |
| Ammonia | High ammonia is closely associated with imbalanced or abnormal microorganisms in your body, most often in your GI tract. See Chapter 6 on CSA and GI testing for approaches you and your doctor can consider in terms of assessing and addressing microbial imbalances. To help your body to deal with high ammonia, consider CBS/NOS Kidney Support capsules, as well as Carnitine. Consider using Magnesium Citrate, charcoal flushes, and low dose Yucca as needed.For low ammonia, increase the protein in your diet. Use AminoAssist spray and/or AminoAssist capsules. Other options for increased protein support are the use of Egg Protein Powder, if you have no egg allergy, or Royal Jelly, if you have no bee allergy. |
| Overall Amino Acids | For low overall amino acids, either you are not eating enough protein and/or your GI tract is not absorbing them well. Consider appropriate diet and supplements to address amino acid support. Consider a CSA test and GI Test to address digestive issues. You can also consider running an Intestinal Permeability test and a Celiac test. Also consider a MAP test to look for ketosis. For low overall amino acids, consider Egg Protein Powder, AminoAssist capsules, and AminoAssist spray for three routes of administration of amino acids. Also, consider Bowel Support nucleotide blend, VitaOrgan, and Royal Jelly, if you have no bee allergies. Ora-Placenta may also be a help to support amino acids. |
| Methionine | Methionine is a critical part of your methylation cycle. Low levels of methionine suggest a need to support both the long route, the pathway that uses the MTR/MTRR enzymes, and the short cut, the BHMT pathway. Methylmate A and short cut support can be added even if lithium is low. Check that lithium is in balance on a HMT before adding extra B12 and Methylmate B for the long route. If you are adding methionine, be sure you have support for the methylation cycle in place so you can process the methionine and homocysteine that is generated as a result of methionine support. AminoAssist spray or AminoAssist capsules can be added for low levels of methionine. The Muscle Fatigue Support compound supplement is also a source of low dose methionine. For methylation cycle support, consider Phosphatidyl Serine Complex (PS/PE/PC), DHA, and All in One. This supports the short cut pathway. Then, Methylmate A can be added, and finally, once lithium is in balance, add extra B12 and Methylmate B. If methionine remains low, you can add sprinkles of Methionine. Check lithium on a HMT prior to adding extra B12 or higher levels of Black Bear Spray or Black Bear Drink, which is a source of B12 and molybdenum. Alternately, high methionine is sometimes seen in those who are ACAT+. The use of ACAT/BHMT capsules may help to restore methionine to healthy, balanced levels. High levels of methionine have been reported to cause increased tryptophan levels, as well as lower serotonin and GABA. Theoretically, this is due to competition for B vitamins, in particular B6 or P5P. Therefore, if methionine levels are high, consider using Ultimate B, and check tryptophan on a UAA, as well as the relative levels of glutamate to GABA. |
| Lysine | Lysine is often used to help with Herpes cold sores. Alternate supports for this can include alternating IMF 1, IMF 2, and IMF 6, or topical Clear Skin spray, to help lower the level of lysine support needed. In addition, some studies suggest that lithium may be a help for Herpes (Amsterdam, 1996). Lysine can impact calcium absorption and retention. Consider a UEE and HMT to look at calcium levels when lysine is being supplemented, or when lysine levels are significantly out of balance. AKAA may lead to high Lysine, so check AKAA levels on a MAP test. If lysine levels are high, yet alpha amino adipic acid is low, consider Ultimate B and/or low dose P5P, as lysine intermediates that build up prior to alpha amino adipic acid can inhibit P5P. If ornithine, cysteine, and carnosine are high along with lysine, then rule out dibasic-aminoaciduria. The use of low dose Citrulline as well as adequate methylation support may help in this case. Rerun a UAA after 4 to 8 weeks to be sure that these dibasic amino acids are in better balance. High oxaloacetate can convert to high lysine and high threonine. If both lysine and threonine are high, consider a MAP test and addressing oxalates. Pay attention to B12 levels and lithium for B12 transport if oxalate issues are suspected. B vitamins can be a help in processing lysine. Consider Ultimate B and/or add each of the B vitamins individually including NADH, Riboflavin-5-Phosphate, B12, and Vitamin PQQ. Vitamin PQQ is a new B vitamin and is included in Ultimate B. Ultimate B includes a natural support for PQQ. For energy, consider CoQ10, Carnitine, and MitoForce. Chervil is another possible source of PQQ as well as a source of vitamin A.For low overall amino acids, support with diet and supplements, and consider a CSA test and GI Test to look for imbalances in your digestive tract and fatty acid processing.For low overall amino acids, consider Egg Protein Powder, AminoAssist capsules, and AminoAssist spray for three routes of administration of amino acids. Also, consider Bowel Support nucleotide blend, VitaOrgan, and Royal Jelly if you have no bee allergies. Ora-Placenta may also be a help to support amino acids. |
| Threonine | High threonine may be associated with high oxalates, so consider running a MAP test. Because high oxaloacetate can convert to both lysine and threonine if both lysine and threonine are high, a MAP test would be suggested, as well as addressing oxalates if they are an issue. Pay attention to B12 levels and lithium for B12 transport if oxalate issues are present. See the suggestions for addressing high oxalate and oxalic acid in Chapter 4. Low threonine may be associated with Clostridia, Pseudomonas, E.coli or Klebsiella. You can consider ruling out these microbial issues with a MAP test, a CSA test and a GI Test. Threonine can be supportive for your immune system. If threonine levels are low, use T cell and B cell support capsules for immune support. If your threonine is high, decrease any added threonine support. Increase B12 once lithium is checked on a HMT because low B12 may be a factor. Also, check leucine levels on this UAA, as high leucine in the absence of high isoleucine or valine, may indicate a need for phosphate. Low phosphate, in turn, can impact alpha KG and oxalates. This is discussed in Chapter 4 on the MAP test in the section on oxalates. High threonine is indirectly related to high oxalate, so consider ATP and B12. Increased threonine can also raise 3 methylhistidine. If microbes are an issue, consider herbal microbial support such as Naturomycin Spray, Naturomycin capsules, and grapefruit seed extract (GSE capsules or GSE liquid). Bay leaf, Paradex, Mycoceutics can also be considered, depending upon the organisms found. You can also consider the full Clostridia program for these organisms. BactiSolve can be considered if you have NO shellfish allergies, EDTA soap or soak daily, along with Malic Acid. |
| Leucine | Leucine, isoleucine and valine are all branched chain amino acids. Generally the levels of all three will track together, so if one is high all three will generally be high, if one is low all three will generally be low. If the three BCAAs, leucine, isoleucine, and valine, are all high, then consider Adenosyl B12 and Biotin to help process them, or use Black Bear Spray and Biotin. There are certain instances in which the level of only one of the three is impacted. If phosphate is low, then only leucine may be increased, but not isoleucine or valine. High leucine, in turn, may increase glutamate, which may increase alpha KG, which may cause hypoglycemia. So, check phosphate levels on UEE and HMT, and check alpha KG on a MAP. If leucine alone is high, then consider ATP and Riboflavin-5-Phosphate to support phosphate levels. Also, check for signs of ketosis on a MAP test when high levels of leucine, isoleucine or valine are noted, as the ketoacids of these amino acids are present on the MAP test. The combination of high levels of one or more of the BCAA on this UAA with high levels of ketoacids on a MAP would suggest possible ketosis and the need to adjust diet as well as consider supporting with Adenosyl B12, Biotin and Special Digestive Enzymes. Specific issues with the breakdown of leucine may cause an overall body odor that smells like “sweaty feet”. Low levels of leucine, its ketoacid AKIC, and low levels of BCAAs in general, may be a factor in absence seizures. If levels of AKIC on a MAP are very low, along with low levels of leucine or BCAAs on this UAA, then consider BCAA support and AminoAssist capsules, again being sure there is no maple syrup smell in your urine due to too much support. This is important because high levels of BCAAs and their respective ketoacids have been implicated in depletion of mitochondrial energy which has significant negative effects. If all three BCAAs are low, then consider low dose BCAA support. Be sure there is no maple syrup smell coming from your urine. If a maple syrup smell is present, then discontinue BCAA support. Be sure that you have sufficient Adenosyl B12 and Biotin in place before adding any BCAAs back. Lack of BCAAs can be a factor in a number of neurological symptoms, including some cases of Bell’s Palsy.For overall low amino acids, consider Egg Protein Powder, AminoAssist capsules and AminoAssist spray for three routes of administration. Also Bowel Support nucleotide blend, VitaOrgan, and if you have no bee allergies, Royal Jelly. Ora-Placenta may also help to support amino acids. |
| Isoleucine | Leucine, isoleucine and valine are all branched chain amino acids. Generally the levels of all three will track together, so if one is high all three will be high, if one is low all three will be low. If the three BCAAs, leucine, isoleucine, and valine, are all high, then consider Adenosyl B12 and Biotin to help process them, or use Black Bear Spray and Biotin. However, there are certain instances in which the level of only one of the three is outside of the normal range. If only isoleucine is high, and not leucine or valine, it may be due to high oxaloacetate, which may indicate a need for more B12. Also look at suggestions for oxalates in Chapter 4 on the MAP test. If all three BCAAs are low, then use low dose BCAA support. Be sure there is no maple syrup smell coming from your urine. If a maple syrup smell is present, then discontinue BCAA support. Be sure that you have sufficient Adenosyl B12 and Biotin in place before adding any BCAAs back. Lack of BCAAs can be a factor in a number of neurological symptoms, including some cases of Bell’s Palsy. Low levels of BCAAs, in particular low levels of leucine, may be a factor in absence seizures. If levels of BCAAs are very low, along with low levels of isoleucine, then consider BCAA support and AminoAssist, again being sure there is no maple syrup smell coming from your urine due to too much support. This is important because high levels of BCAAs and their respective ketoacids have been implicated in depletion of mitochondrial energy which has significant negative effects. For overall low amino acids, consider Egg Protein Powder, AminoAssist capsules and AminoAssist spray for three routes of administration. Also Bowel Support nucleotide blend, VitaOrgan, and if you have no bee allergies, Royal Jelly. Ora-Placenta may also help to support amino acids. |
| Valine | Leucine, isoleucine and valine are all branched chain amino acids. Generally the levels of all three will track together, so if one is high all three are high, if one is low all three are low. However, there are certain instances in which the level of only one of the three is outside of the normal range. If only valine is high, it may be due to high pyruvate, so consider MitoForce and Ultimate B. In addition, if only valine is high, consider using ACAT/BHMT capsules to help with processing Co A, because valine is not moving to leucine and Isoleucine. If all three BCAAs are high, then consider Adenosyl B12 and Biotin to help process them. Alternately, you can use Black Bear Spray and Biotin. If all three BCAAs are low, then consider low dose BCAA support. Lack of protein in the diet leads to a general lack of all amino acids. Certain neurological syndromes may indicate low BCAAs, such as trigeminal neuralgia, Bell’s Palsy, and TMJ, among others. Be sure there is no maple syrup smell coming from your urine. If a maple syrup smell is present, then discontinue BCAA support. Be sure that you have sufficient Adenosyl B12 and Biotin in place before adding any BCAAs back.For overall low amino acids, consider Egg Protein Powder, AminoAssist capsules and AminoAssist spray for three routes of administration. Also Bowel Support nucleotide blend, VitaOrgan, and if you have no bee allergies, Royal Jelly. Ora-Placenta may also help to support amino acids. |
| Phenylalanine | A “musty odor” emanating from your body can be a sign of excess phenylalanine. High levels of phenylalanine have a range of neurological consequences, so limit your ingestion of aspartame even if your phenylalanine is not high. High phenylalanine may signal a need for more BH4, because BH4 helps to convert phenylalanine to tyrosine and then to dopamine. Especially if tryptophan, tyrosine, and phenylalanine are all high, consider MTHFR A1298C Liver Support capsules, along with BH4. If you have no bee allergies, you can also consider Royal Jelly. You can consider running a Neopterin / Biopterin Profile Urine Test to get your biopterin level as an additional indicator for a need for BH4 support. Pay special attention to aluminum on a HMT and a UEE, because aluminum has a negative impact on BH4 levels. Check that bacterial imbalances are not an issue, as this may cause increased aluminum levels, which in turn may reduce BH4. Also, consider using MetalAway to help with healthy BH4 levels and to address aluminum. |
| Tryptophan | High tryptophan, along with phenylalanine and tyrosine, may signal a need for more BH4, because BH4 helps to convert phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan into dopamine and serotonin respectively. Consider using MTHFR A1298C Liver Support capsules along with BH4. If you have no bee allergies, you may use Royal Jelly. If tryptophan is either too high or too low, consider running a NT test to check on serotonin, and a MAP test to look at the breakdown products from serotonin, such as 5HIAA. The approach I use when looking at tryptophan is to look at the balance between the available starting material for serotonin production, i.e., tryptophan, in conjunction with the actual levels of serotonin on a NT test, counterbalancing these two values with the level of serotonin breakdown products on a MAP. This gives me a picture of what is going on with serotonin, the serotonin turnover, as opposed to just looking at the level of tryptophan or of its neurotransmitter, serotonin. Low serotonin has been implicated in OCD behaviors, as well as depression. When niacinamide levels are too low, it can cause the breakdown of tryptophan, so consider using Ultimate B, NADH and/or Niacinamide. There is a delicate balance with respect to tryptophan breakdown and vitamin B3 levels which can be affected by bacteria. One of the breakdown products from tryptophan, kynurenic acid, is calming, but in the presence of B6 or pyridoxal-5-phosphate, kynurenic acid will convert to quinolinic acid, which is an excitotoxin. I have suggestions for dealing with high quinolinic acid in the quinolinic acid section of the MAP test description in Chapter 4. Conversely, high levels of methionine may deplete B6 and cause high levels of tryptophan with less conversion to serotonin. Ultimate B is a low dose source of B6 that can be used for support. Also, a Neopterin / Biopterin Profile Urine Test can be run, as well as looking for indicators for BH4 support on a MAP test. High methionine is often seen for those who are ACAT +, in these cases the use of ACAT/BHMT capsules may also help to get methionine in better balance, which in turn can impact tryptophan. Pay special attention to aluminum on a HMT and a UEE, as aluminum may further reduce BH4 levels. Check that bacterial imbalances are not an issue, as they may relate to high aluminum, which in turn reduces BH4 production. Also, consider using MetalAway to help enhance BH4 levels and to address aluminum.For low tryptophan, you can consider Egg Protein Powder, AminoAssist capsules, AminoAssist spray, and low dose SeroMood as needed. |
| Taurine |
For low taurine, be sure full methylation cycle support is in place. Basic methylation support includes All in One, Phosphatidyl Serine Complex (PS/PE/PC), DHA and Methylation Support nucleotide blend. You may also use low dose Methylmate A while working to get lithium in balance. Once lithium is shown to be in balance on a HMT, then consider low dose Methylmate B, along with extra B12. High taurine may affect body temperature. High taurine, along with high levels of alanine and serine, have been implicated in lowering body temperature. The mechanism by which this temperature lowering effect occurs is not well defined. Theories put forth include the inhibitory impact of high taurine on the hypothalamus, on inhibitory properties that may play a positive role in seizure regulation, or because high taurine may inhibit GABA transport. It is also possible that hydrogen sulfide, which is generated from high taurine, is the pathway by which it lowers body temperature. High levels of taurine can put pressure on the remainder of the transulfuration pathway, creating a need for Molybdenum and B12 in order to process toxic sulfur groups. If taurine levels are high, stop any added high dose taurine. The amount of taurine in All in One is not high dose. Some low level taurine is important in terms of helping to balance your system and aid in reducing possible seizure activity. If you are not adding taurine, yet levels are above the 84th percentile, then consider low dose CBS+ nucleotide blend. Those who are CBS C699T, CBS A360A, or CBS 212 may tend toward high taurine levels. This can cause problems with sulfur processing and potentially deplete B12 and molybdenum. High levels of taurine also can cause low levels of GSH. So, in addition to low dose CBS+ nucleotide blend, also consider using GSH. Rerun a UAA 6 to 8 weeks after starting CBS+ nucleotide blend to be sure your taurine is in the normal range. As always, work with and defer to your own doctor when working on taurine levels. Also consider checking zinc levels, because increased taurine may lead to low zinc. Low zinc can throw off your zinc/copper ratio and may affect your ability to pay attention. Also, low zinc is a particular issue for adolescent males, as that group needs more zinc. Low zinc is also an issue for those with high levels of cadmium, as cadmium can replace zinc in important reactions in your body.Taurine may also be elevated due to infection. TNF alpha, an important inflammatory mediator, can increase CBS enzyme activity, which in turn may increase taurine. If you are not adding taurine, and you have no specific CBS SNPs (A360A, C699T, or 212), yet taurine is still high, then infection may be the cause. In this case your GI tract is the first place to look, so consider running a CSA test and GI Test. Excess taurine may increase hydrogen sulfide (H2S) that is also produced in the in the transsulfuration pathway. H2S increases NMDA receptor responses which may cause over excitation of nerves. You can consider using Nerve Calm nucleotide blend, BeCalm Spray, and GABA Balance capsules if needed. H2S is catabolized by thiosulfate reductase in the mitochondria. The sulfite generated is then oxidized to sulfate by sulfite oxidase (SUOX), which can be helped by B12 and Molybdenum support. Low dose Ion Transport compound and/or low dose Wasabi may be helpful for thiosulfate processing.H2S can trigger potassium dumping, so consider checking a HMT and UEE, especially because low potassium can be a factor in aggression.Potassium needs to be supported when you are taking lithium.H2S can also cause direct DNA damage, so if taurine is very high, consider a 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) test for DNA damage. Support with Quercetin and Ultifend may be helpful if DNA damage is a concern. H2S can also deplete glutathione, which may already be low because of high taurine. Low glutathione can free up iron, which may increase problem gut bugs because iron drives bacterial virulence. So, consider SHMT support for iron issues. High levels of H2S have also been found in Down’s syndrome.Increased H2S can be found in Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS), so consider addressing H2S, as well as support for nitric oxide. The nitric oxide supports can include Arginine and/or Citrulline, depending on their levels on your UAA test. You also can consider BH4 support for optimal nitric oxide cycle function. Low nitric oxide has been implicated in some cases of POTS.High taurine may also have an inhibitory effect on GABA transport.For those with the more rare condition of Huntington’s Disease (HD), consider that HD genes interact with the CBS gene and may cause high taurine because of this. Also, trehalose may help with the glutamate that is produced secondary to HD. BeCalm Spray and Nerve Calm nucleotide blend may also be helpful. Again, work with your doctor on taurine levels that are too high. Consider the use of low dose CBS+ nucleotide blend. It is important to rerun a UAA 6 to 8 weeks after starting CBS to check that taurine levels are in a normal range. Finally, I want to take a few moments to explain more thoroughly the science behind these CBS SNPs. This can be such a critical SNP that it is important to understand the logic regarding increased CBS activity from these mutations (C699T, A360A and CBS 212), as they have the capacity to ‘drain’ intermediates from the methylation cycle, put pressure on sulfite processing, as well as decrease glutathione levels. There has been some confusion regarding CBS “upregulations”. This may be in part because many SNPs impair the function of an enzyme. In the case of these particular CBS SNPs, these mutations increase the activity of the enzyme, rather than impairing it, as is the case with many mutations. When someone is CBS C699T + or ++, it is easy to see the impact of that “upregulation” by methionine loading and then running a UAA test. You will see taurine levels that are very, very high. Many of those who are CBS C699T + will actually show extremely high taurine even in the absence of methionine loading, or with simple basic methylation support. I do not use or recommend methionine loading, but I mention this if you want to see for yourself the impact of that SNP. According to published, peer reviewed literature, the C699T mutation is what is known as a silent mutation. The change at a molecular level from a C to a T, does not cause a change in the amino acid sequence, so it is considered a synonymous or silent mutation. Often silent mutations either have no impact or are regulatory in nature. Part of the reason I choose this SNP, as well as A360A and CBS 212 for my panel, is that I am most interested in regulatory mutations. Clearly CBS C699T has an impact which is very obvious in terms of taurine levels on a UAA after methylation support or methionine loading. The methionine loading effect may not be observed for those who are MTHFR C677T + or ++, and in this case 5 methyl THF loading would show the effect. Studies looking at the C699T and A360A SNPs, suggest that they are in fact changes that increase CBS activity. “…The 699C–>T and 1080C–>T (A360A) polymorphisms may be in linkage disequilibrium with regulatory elements that upregulate CBS gene transcription.” (Aras, et al Clinical Genetics, 58: 455–459, 2000). Additional literature reinforces the concept that CBS C699T+ or ++ has the ability to increase enzyme activity because CBS C699T+ is in “strong linkage disequilibrium” with regulatory elements, which is logical since it is located in the gene’s promoter region. More specifically, CBS C699T+ is suggested by articles to be in strong linkage disequilibrium with the 68 bp insert that causes an increase in CBS activity. According to Fredrikson et al, “Our observation that the 68 bp insertion is in strong linkage disequilibrium with the CBS c699T is in accordance with earlier reported data…Thus the metabolic phenotype of the CBS c699T polymophism is similar to that of the 68 bp insertion” (Hum. Mutat., 28: 856–865, 2007). Studies state that the 68bp insert causes alternate splicing of the gene such that a shorter final product is produced. The shorter construct has been stated to be “constitutively” active, which means it is constantly active. (Shan Hum Mol Genet. Mar 15;10(6):635-43,2001). Thus, increased activity would be expected to result in higher taurine and lower homocysteine, which is what is observed for the 68 bp insert, as well as the C699T mutation. (Kruger et al, Mol Genet Metab. May;70(1):53-60, 2000) Furthermore, literature indicates that the 68bp insert counteracts the increase in homocysteine due to the MTHFR C677T mutation. This fits with an increase in CBS activity for those with the 68bp insert that in turn is in linkage disequilibrium with the C699T mutation. (De Stefano, Ann Hum Genet. 1998 Nov;62(Pt 6):481-90. |
| Cysteine | If only cysteine is high, be sure there is sufficient support in the transsulfuration pathway for the processing of sulfur groups. These supports consist of B12 and Molybdenum, Black Bear Spray or Black Bear Drink. Check that lithium is in balance on a HMT before building up the dose of B12.Cysteine processing can ultimately produce pyruvate that feeds into the Krebs cycle. Be sure that sufficient B complex, such as Ultimate B, is in place to allow pyruvate to enter the Krebs cycle. This can be followed on a MAP test. If ornithine, lysine, and carnosine are all high in addition to cysteine, then consider and rule out dibasic aminoaciduria. The use of low dose Citrulline, as well as adequate methylation support, may help in this case. Rerun a UAA after 4 to 8 weeks of support to be sure that these dibasic amino acids are in better balance. If cysteine is low, then consider methylation cycle support. Basic methylation support includes All in One, Phosphatidyl Serine Complex (PS/PE/PC), DHA and Methylation Support nucleotide blend. Methylmate A can also be added before lithium is in balance. Once lithium is shown to be in balance on a HMT, then use low dose Methylmate B, along with extra B12. |
| Arginine | Excess arginine can be generated from urea cycle activity. If this is the case and arginine levels are high, then consider MTHFR A1298C Liver Support capsules, as well as BH4. Also, excess arginine excretion can be seen in some cases of H. pylori infection. Rule out H. pylori with testing, and look for other symptoms of H pylori, including high levels of suberic on a MAP test, wide swings in pH on a CSA test and GI Test, and direct H. pylori testing. If lysine is being supported, as is often the case in the presence of Herpes, then balance any lysine support with an equal amount of arginine support, as lysine can antagonize arginine levels. Look at creatinine levels if arginine is high, because arginine from the urea cycle is available to produce creatinine. If creatinine is very high, then consider kidney support: low dose Kidney Support nucleotide blend, Ora-Kidney, and dandelion leaf. Include SHMT support and Rhodiola. Increased urea cycle activity can cause increased levels of aspartate. Aspartate can then feed into the Krebs cycle to increase the level of oxaloacetate, which converts into oxalic acid. High aspartate can also result in elevated beta alanine. Beta alanine leads to increased levels of carnosine and anserine. Elevated histidine due to decreased tetrahydrofolate (THF) also increases the formation of anserine. See notes on Chapter 4, the MAP test, for suggestions for high oxalate. Arginine may have a positive impact on potassium levels. Those who struggle with consistently low potassium, especially athletes, may consider low dose arginine support if levels of arginine are low. Arginine and citrulline both can help to produce nitric oxide in your body, provided that there is sufficient BH4 present in your system. Extremely low levels of nitric oxide have been associated with aggressive behavior in animal models, and nitric oxide can impact blood pressure, so maintain normal, healthy levels, as opposed to extremely high or low levels. Using 5-methyl THF as in Methylmate B has been reported to help with healthy nitric oxide levels by helping to support nitric oxide synthase (NOS). Low nitric oxide has been implicated in some cases of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS). In addition, the combination of low nitric oxide and increased H2S is found in POTS, so consider addressing both H2S as well as nitric oxide.Lack of arginase activity can also elevate arginine levels. Arginase requires manganese for activity, so check manganese levels on a UEE and HMT. Glucosamine/Chondroitin Plus is a good source of manganese, as well as a source of support for your GI tract lining.High levels of arginine may be associated with muscle stiffness, and in extreme cases, developmental delay and mental retardation. Some articles suggest a see saw relationship between arginine and alpha KG. If arginine is very high or low, check that alpha KG is in balance on a MAP test. |
| Histidine | Low tetrahydrofolate (THF) levels can cause elevated histidine. Elevations in histidine, in turn, cause increased levels of anserine and carnosine. So, high histidine along with high anserine and carnosine may indicate a need for THF. Consider using All in One or Ultimate B. In addition, check FIGLU levels on a MAP test, as FIGLU will also climb If there is not sufficient THF. Thus, high FIGLU may be an indirect sign of excess histidine. High levels of histidine may depress the levels of other amino acids, as well as be related to high cholesterol. A GI function test can be run to look at cholesterol levels. In addition, high histidine can translate to increased histamine, which is a factor in allergic reactions and inflammation. This can be exacerbated by low copper, because copper is needed for mono amine oxidase (MAO) activity, which breaks down histamine. Also, check taurine, because high taurine may indicate increased CBS enzyme activity. Increased CBS activity can generate excess H2S, which may decrease MAO enzyme activity and the breakdown of histamine. This may increase histamine levels. Quercetin can help with high histamine, but quercetin can inhibit COMT, so this can be non-optimal for those who are COMT ++ who have slow COMT activity. Cherries are a natural source of quercetin, but while cherries may help with inflammation and some forms of arthritis, high quercetin levels may cause problems for those who are COMT ++. Licorice can also inhibit MAO, so along with low copper and high H2S, licorice may reduce the breakdown of histamine, allowing higher levels to accumulate. If allergic reactions are an issue, low dose Hyper-Balancing nucleotide blend can be considered. |
| Alanine | High alanine may be due to lack of ATP, NADH, and/or B complex to move it along in its conversion to pyruvate for entry into the Krebs cycle. See Chapter 4 on MAP testing for more on this topic. Consider using MitoForce, Ultimate B, and/or Riboflavin-5-Phosphate. High alanine may also be due to excess 5HTP or tryptophan support, as tryptophan can breakdown to alanine. Alanine feeds into pyruvate for the Krebs energy cycle, so if pyruvate is low on a MAP test, it may be related to low levels of amino acids in general, and alanine in particular. Alanine may be useful support for ketosis, especially post exercise ketosis. Markers for ketosis can be checked on a MAP test. In some cases, a sweet, fruity smell to the breath is an indicator of ketosis. AminoAssist includes alanine in its propriety blend of amino acids. |
| Aspartate & Asparagine | In the presence of ammonia, aspartate converts to asparagine. So, if aspartate is low and asparagine is high, consider support to address ammonia. Low dose CBS/NOS Kidney Support capsules (NOT the nucleotide blend) may be helpful. With low levels of ammonia, aspartate may increase. Aspartate can then feed into the Krebs cycle to increase the level of oxaloacetate and oxalic acid. If aspartate, asparagine and threonine are all high, this suggests high oxaloacetate/oxalic acid, which in turn suggests that you may need B12 support. Check cobalt and lithium on a UEE and a HMT. Support B12 and lithium as needed, using All in One, BeCalm Spray, and a source of B12. High aspartate can also result in elevated beta-alanine. Elevated beta-alanine leads to increased levels of carnosine and anserine. So high levels of beta-alanine, carnosine and anserine on a UAA may be related to a need to address aspartate. Along with glutamate, aspartate is an excitotoxin that can over excite nerves. Aspartame, the artificial sweetener, increases your levels of aspartate. Supplementation to address high aspartate is similar to that for high levels of glutamate. Consider support to address aspartate as an excitotoxin, such as Nerve Calm nucleotide blend, Be Calm Spray, and GABA Balance capsules. High asparagine or aspartate may be due to a lack of ATP, NADH, and B complex. Consider using ATP and NADH or MitoForce, along with Ultimate B. Also, eliminate sources of aspartate and aspartame. Supplement to decrease glutamate and increase GABA if they are unbalanced. |
| Glutamine & glutamate | Excess glutamate can over excite your nerve cells, causing excitotoxicity. I have spoken and written about this in many places. The levels of both glutamine and glutamate need to be considered when looking for causes of excitotoxicity, because they convert into one another. The enzyme glutaminase converts glutamine into glutamate, and in the presence of ammonia and ATP, glutamate is converted back into glutamine. The supplements that may help with glutamate/GABA balance are Nerve Calm nucleotide blend, Be Calm Spray, and GABA Balance capsules. Valerian root may be helpful in conjunction with GABA. Pycnogenol, Grape Seed Extract and Resveratrol may also be used. Support Carnosine if your levels are low, because carnosine may decrease glutamate transport into the cells. Jujube & CoQ10 may also help control excess glutamate. KuShen tea is also reported to help with excess glutamate. Eliminate sources of glutamate and excitotoxins. Also, check a HMT and UEE for the levels of minerals that help with glutamate and calcium balance, such as Zinc, Magnesium, and Lithium. According to the literature, creatine may help pull down glutamate, so consider Creatine support if your creatinine levels are low. If your level of phosphate is low, then leucine may be increased, which, in turn, may increase glutamate and alpha KG, and be associated with hypoglycemia. Check hydroxyproline levels. High hydroxyproline can increase glycine and glutamate. When glutamate is high, then glycine can exacerbate the effects of glutamate, so check glycine levels. Use SHMT support as needed to help with glycine balance. H2S increases NMDA receptor responses, so it is important to check taurine levels to be sure there is not too much generation of H2S from taurine. See suggestions for balancing high taurine levels if this is an issue. Be sure there is sufficient Molybdenum and B12 to process sulfites. You can use Black Bear Spray or Black Bear Drink for low dose molybdenum and B12 support. Check lithium before adding high dose B12.High levels of thyroxine (T4) inhibit glutamate dehydrogenase, which turns glutamate into alpha KG. This can increase glutamate levels and decrease alpha KG. T4 is contained in Synthroid and other prescription thyroid. Consider a CSA test and GI Test because imbalances in gut microbes can also affect thyroid hormone production. |
| Cystine | Cystine is the oxidized form of cysteine, so high cystine may indicate both high levels of cysteine and pro oxidant conditions in your body. Consider Ultifend and NADH, as well as other anti-oxidants such as Spirulina and Pycnogenol to help with oxidation. Less cystine or cysteine relative to serine has been noted in some cases of psychosis. A high serine to cysteine ratio, 1.5 to 1 versus 1 to 1, was noted in the literature to be associated with psychosis. Consider running an Oxidative Damage test when high levels of cystine are seen. |
| Glycine | If either serine or glycine are higher than most other amino acids, consider SHMT support. Also, limit iron, and consider using All in One as a low dose source of nucleotides. When high glycine is observed it is also important to check the levels of methylmalonic acid (MMA), succinate, and benzoic acid on a MAP test. Excess levels of glycine can combine with benzoic to form hippuric acid (benzoic acid is used as a food preservative and is naturally found in a number of foods especially berries). While increased hippuric acid in the urine is generally accepted to be due to microbial issues, it can also be due to reactions that can occur secondary to high glycine (combining with benzoic in the system) to produce excess hippuric acid. MMA converts to succinate in the presence of B12. When succinate combines with glycine it generates porphyrins. Thus increased levels of MMA and/or succinate can ultimately lead to increases in biochemical porphyrin products after reaction with excess glycine. If high levels of porphyrins are seen on a porphrin test it is important to check glycine levels to determine if high glycine along with high citric acid intermediates (ie succinate) are the actual source of the high porphyrins. Keep in mind that certain nutritional supports will also increase glycine levels which in turn may influence the levels of biochemical products such as hippuric and prophryrins. High levels of support with trimethylglycine (TMG), or the direct supplementation with glycine may increase both glycine and sarcosine, which can in turn increase porphyrin and hippuric acid levels. TMG is also called betaine, which is contained in the digestive support Betaine HCl. |
| Tyrosine | Tyrosine is important in the formation of dopamine, a NT which plays a critical role in attention, focus, reward motivated behavior, as well as mood. Cross check your levels of tyrosine with dopamine on a NT test, and with the break down products of dopamine on a MAP test for an overall sense of the status of the pathway from tyrosine to dopamine. For low tyrosine levels, consider AminoAssist support. If needed, you can consider low dose support for dopamine. High levels of tyrosine may generate a smell of “cabbage” from your body. High levels of tyrosine may indicate a lack of BH4 which is needed to convert tyrosine to dopamine. Suspect a lack of BH4 particularly if tryptophan and phenylalanine are also elevated. Low dose BH4 as well as MTHFR A1298C Liver Support capsules may be a help when this is the case. |
| Serine | If either serine or glycine are higher than most other amino acids, consider SHMT support. Also, limit iron, and consider All in One as a low dose source of nucleotides. High levels of 5,10methylene THF may cause increases in serine. This should be kept in mind, because imbalances in serine may be a factor in some cases of psychosis. Less cysteine or cystine relative to serine has been observed in psychosis. A serine to cysteine ratio of 1.5 to 1 versus 1 to 1 was noted in the literature to be associated with psychotic thought disorder. |
| Proline | Excess proline can convert to glutamate, so be sure you are not using excessive proline support. If glutamate is high along with proline, consider Nerve Calm nucleotide blend, Be Calm Spray, and/or GABA Balance capsules. Also, be sure that magnesium is higher than calcium and zinc is higher than copper on a UEE or HMT. Both zinc and magnesium can help to balance calcium, which can exacerbate glutamate toxicity. Also, check that lithium is in balance on a HMT. |
| Ethanolamine | Often the levels of ethanolamine are high for those who are ACAT+, so consider ACAT/BHMT capsules and/or low dose Cholacol when this is the case. Also, you can consider using Policosanol, Riboflavin-5-Phosphate, ATP, SAM-e, and/or MitoForce when ethanolamine is high.For low levels, consider Phosphatidyl Serine Complex (PS/PE/PC) as well as SAM-e. |
| Alpha Aminoadipate | High levels of lysine, too much lysine support, or not enough alpha KG, may cause high alpha aminoadipate. Ultimate B may help in balancing this pathway. Check alpha KG levels on a MAP test and see suggestions for alpha KG support if indicated by the values found there. Also, Ultimate B serves as a source of low dose vitamin PQQ, which may help with lysine/alpha aminoadipate balance. Alpha aminoadipate may inhibit the enzymes glutamine synthetase and gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase. Thus, high levels of alpha aminoadipate may cause increases in glutamate and decreases of GSH. It may also cause tryptophan to rise. In addition, alpha aminoadipate has been reported to decrease the level of kynurenic acid, which is calming and helps to modulate excitotoxins, as well as to help with seizure activity. Since alpha aminoadipate may lower kynurenic acid levels, consider using Nerve Calm nucleotide blend and Be Calm Spray when alpha aminoadipate levels are high. If lysine levels are high, yet alpha aminoadipate is low, consider using Ultimate B and/or low dose P5P, because lysine intermediates that build up prior to alpha amino adipate can inhibit P5P. |
| Beta-alanine | High levels of aspartate may cause increases in beta-alanine. High levels of beta-alanine may also be due to too much carnosine. A high ratio of uridine to thymidine in your body may also lead to high levels of beta-alanine. Lack of methylation capacity in your body results in your having too few methyl groups. This may generate more uridine relative to thymidine in your system. Thymidine is 3-methyl uracil, uracil that has been methylated at the 3 position. Use methylation cycle support to address this.Basic methylation support includes All in One, Phosphatidyl Serine Complex (PS/PE/PC), DHA, and Methylation Support nucleotide blend. Low dose Methylmate A can be added before lithium is in balance. Once lithium is shown to be in balance on a HMT, then use low dose Methylmate B along with extra B12. Beta-alanine may compete with GABA transport, so consider using Be Calm Spray and GABA Balance capsules, particularly if GABA levels are low along with high beta-alanine. Low levels of beta-alanine may indicate a need for low dose Carnosine, as well as low dose Muscle Support nucleotide blend. |
| Beta-aminoisobutyrate | Beta-aminoisobutyrate is a breakdown product of thymidine. Excess thymidine may be secondary to SHMT imbalance, and can also lead to high levels of beta aminoisobutyrate. SHMT enzyme activity may be increased due to iron, so check iron levels on a HMT and UEE. Consider using SHMT Spray and AHCY/SHMT compound. Also use basic methylation support, which includes All in One, Phosphatidyl Serine Complex (PS/PE/PC), DHA, and Methylation Support nucleotide blend. Low dose Methylmate A can be added before lithium is in balance. Once lithium is shown to be in balance on a HMT, then use low dose Methylmate B along with extra B12. |
| Anserine & Carnosine | Increased levels of carnosine and anserine may be due to high beta-alanine. High beta-alanine may be due to excess aspartate. So, check to see if aspartate is high when you have high carnosine or anserine. Consider support to help address aspartate if it is high. Supports can include Nerve Calm nucleotide blend, Be Calm Spray, and GABA Balance capsules. High aspartate may also be due to a lack of ATP, NADH, and B complex. Consider using ATP and NADH or MitoForce, along with Ultimate B. Also, eliminate sources of aspartate and aspartame. Supplement to decrease glutamate and increase GABA if they are unbalanced. A high ratio of uridine to thymidine in your body may also lead to high levels of beta-alanine. Lack of methylation capacity in your body results in your having too few methyl groups. This may generate more uridine relative to thymidine in your system. Thymidine is 3-methyl uracil, uracil that has been methylated at the 3 position. Use methylation cycle support to address this. Basic methylation support includes All in One, Phosphatidyl Serine Complex (PS/PE/PC), DHA, and Methylation Support nucleotide blend. Low dose Methylmate A can be added before lithium is in balance. Once lithium is shown to be in balance on a HMT, then use low dose Methylmate B along with extra B12. If carnosine is low, support with Carnosine, as carnosine may help with glutamate issues. In addition, be sure sufficient methylation support is in place, along with low dose THF. THF is found in All in One and Ultimate B.A lack of THF can cause increases in histidine. The breakdown of histidine then may cause higher levels of beta alanine, methylhistidine, anserine, and carnosine.If anserine and carnosine are excessively high, while FIGLU on a MAP test is very low, consider that histidase may not be functioning optimally. Be sure copper is not low, as histidase needs copper to function. Rule out a histidase deficiency if levels do not balance with methylation support as well as the supports suggested above. Recall that excess histidine can increase cholesterol levels, and cause issues with histamine and sensitivity.If carnosine is high along with high ornithine, lysine and cysteine, rule out dibasic aminoaciduria. High carnosine may also reflect a need for more muscle support, especially if beta-alanine is also high. If this is the case, consider low dose Muscle Support nucleotide blend as well as Muscle Fatigue Support compound. |
| Gamma-aminobutyrate | If gamma-aminobutyrate (GABA) levels are low, support with GABA, such as GABA Balance capsules and Be Calm Spray. Also, look at glutamate levels and work to balance high glutamate with GABA as needed. Toxic doses of manganese can impact both GABA and taurine levels, and affect their transport into the cell. If an individual is intolerant to GABA supplementation in spite of symptoms that suggest a need for GABA support, then check manganese levels to be sure they are not high. If very high manganese levels are present, run a Water Elements Test to look for the source of manganese. |
| Hydroxyproline | Hydroxyproline plays a role in collagen formation and is produced from proline by vitamin C. If levels are low, consider Vitamin C with rose hips. High levels of hydroxyproline may be due to high levels of sulfur amino acids. This may also indicate a need to support with Molybdenum and B12 to process sulfur groups. You can also use Black Bear Spray or Black Bear Drink for low dose molybdenum and B12 support. Check lithium before adding high dose B12. Check sulfur on a HMT and UEE. High hydroxyproline can increase both glycine and glutamate, so check the levels of these two substrates. High levels of hydroxyproline excretion may be related to bone or collagen processing, so consider low dose Bone nucleotide blend, Bone Support capsules, and the addition of Riboflavin-5-Phosphate. |
| Citrulline | If levels of citrulline are low be sure that dibasic aminoaciduria is not an issue. Consider support with AminoAssist and low dose additional Citrulline. If levels are high, then check to see if arginine is also high. Both amino acids being high may indicate a need to support arginase with low dose Manganese. If ornithine is high, along with high citrulline and arginine, there may be aluminum present in your body that is blocking the function of the Krebs Citric Acid Cycle. The Krebs cycle may be shunting substrates into the urea cycle. A MAP test can be run to look at Krebs cycle intermediates. In this case, consider support to address aluminum. There is a list of suggestions on the HMT and UTM for addressing aluminum. In addition, consider BH4, as well as MTHFR A1298C Liver Support capsules, to help to support urea cycle production of less pro oxidant species. Arginine and citrulline both can help produce nitric oxide in your body, provided that there is sufficient BH4 present. Extremely low levels of nitric oxide have been associated with aggressive behavior in animal models. Nitric oxide can impact blood pressure. Maintain normal, healthy levels, as opposed to extremely high or low levels. Using 5-methyl THF, Methylmate B, has been reported to help with healthy nitric oxide levels by helping to support nitric oxide synthase (NOS). Low nitric oxide has been implicated in some cases of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS). In addition, the combination of low nitric oxide and increased H2S is found in POTS, so consider addressing both H2S as well as nitric oxide if POTS is a concern. |
| Phosphoethanolamine | For low levels, consider Phosphatidyl Serine Complex (PS/PE/PC) as well as SAM-e. |
| Phosphoserine | For low levels, consider Phosphatidyl Serine Complex (PS/PE/PC) as well as Riboflavin-5-Phosphate. |
| Methionine Sulfoxide | High levels of methionine sulfoxide may indicate a need for additional ATP, or MitoForce. Also, consider Ultifend, NADH, and GSH to help with oxidative stress, disulfides such as H2S, and to lower the levels of methionine sulfoxide in your body. It has been suggested that methionine sulfoxide is a factor in aging. Levels do increase with age. |
| Cystathionine | Homocysteine is converted to cystathionine by Cystathionine Beta Synthase (CBS). Cystathionine is, in turn, converted into cysteine. Both reactions are increased with B6, and the overall pathway, called the Transsulfuration Pathway, is a reflection of CBS activity. Those who have an up regulation in CBS enzyme activity by virtue of a mutation in the genes that encode for this enzyme, or who are using high levels of B6, or who have high levels of TNF alpha, tend to have higher levels of cystathionine, cysteine, and/or taurine. High TNF alpha can be caused by infection, such as those that are commonly found in the GI tract. Look at the overall balance of cystathionine, cysteine, and taurine in determining if a decrease in B6 support is indicated, or if CBS+ nucleotide blend is needed. Also, consider a CSA test and GI Test to address bacterial issues that may be impacting cystathionine levels. Cystathionine is an intermediary step on the way to cysteine. As such, it may or may not be high. This is the reason that you look at cystathionine, plus cysteine and taurine, for an overall sense of whether or not this pathway is over active. If cysteine levels get too high due to over activity, you may also see high taurine and low GSH. See information regarding taurine levels in this chapter for additional support suggestions. |
| 1-Methylhistidine &3-Methylhistidine | 1 methylhistidine can climb secondary to high aspartate levels. There are many reasons why aspartate may be elevated, and many suggested supports for it in the aspartate section of this chapter. 3 methyl histidine may increase because of high threonine, which may be secondary to high oxalate, which in turn is related to a need for B12. Additional information about oxalates and addressing high levels of oxalates can be found in Chapter 4, the chapter describing the MAP test. If levels of both 1 and 3 methylhistidine are low, and if the use of AminoAssist is not sufficient to cause levels to get into better balance, then consider low dose histidine support. A high level of both 1 and 3 methylhistidine may reflect a need for muscle support. You and your doctor can consider using low dose Muscle Support nucleotide blend and Muscle Fatigue Support compound. |
| Homocystine | Homocystine is the oxidized form of homocysteine. High levels suggest both a need for antioxidants, as well as a need for methylation support to process homocysteine to methionine via the long and short cut around the cycle. Consider Ultifend and NADH for antioxidant support. Basic methylation support includes All in One, Phosphatidyl Serine Complex (PS/PE/PC), DHA, and Methylation Support nucleotide blend. Low dose Methylmate A can be added before lithium is in balance. Once lithium is shown to be in balance on a HMT, then use low dose Methylmate B along with extra B12. Also, consider running the Oxidative Damage test to see how problematic the pro oxidant conditions are. |
| Sarcosine | Sarcosine levels may climb with the use of trimethylglycine (TMG), as well as when glycine is an issue. High levels of support with TMG may increase both sarcosine and glycine, which can in turn increase porphyrin and hippuric acid levels. TMG is also called betaine, which is contained in the digestive support Betaine HCl. Consider SHMT support, Phosphatidyl Serine Complex (PS/PE/PC), and DHA, rather than TMG, to support the pathway between homocysteine and methionine in the methionine cycle. TMG is a methyl donor and should be avoided especially in people who are COMT+. When rhodiola is used to balance high creatinine, the levels of sarcosine may climb as creatinine levels fall. If too much choline support is in place, it may also cause sarcosine to climb. |
Looking for a particular supplement or word in this chapter?
Enter your search term here to highlight it throughout the page:
Please be patient as it may take a few moments to search through all of the content.
To search the entire site, not just this chapter, please click the magnifying glass icon
next to ‘Resources’ at the top of the page.
Related Tests to Run
The MAP test discussed in Chapter 4 gives useful information in conjunction with a UAA about methylation cycle support, as well as the balance of the Krebs Citric Acid cycle. Amino acids feed into the Krebs energy cycle. The combination of MAP data along with UAA data gives a more complete picture of amino acid balance and how they are entering into the energy cycle.
Looking at tryptophan and tyrosine levels on a UAA, in conjunction with having the levels of their respective neurotransmitters from neurotransmitter testing, in addition to having information about the breakdown products of dopamine and serotonin from a MAP test, gives a much more comprehensive picture of neurotransmitter balance than you get from any one test in isolation.
In a similar fashion, the levels of lithium, potassium and manganese on a HMT and UEE can be considered with respect to one another, uncovering much more information than either test alone. Having accurate and comprehensive information about the levels of these minerals helps you to interpret data from a UAA. For example, you will be able to discern very quickly if elevated arginine is due to a lack of manganese, or if you must continue to look for other factors. It is very helpful to be able to rule in or rule out single causes of what otherwise may be complex conditions.